Abstract

Background: Standard therapeutic regimens for older HL patients (pts) may confer significantly increased toxicity and inferior survival compared with younger pts. Reported complete remission (CR) rates for older pts are 45-76% with 2-year (yr) progression-free survival (PFS) rates of 50-71% (eg, Evens et al. Blood 2012). With a goal of improving outcomes for older cHL pts, this multicenter phase 2 study tested Bv given sequentially before and after standard AVD chemotherapy.
Methods: Older pts (aged ≥60 yrs) with stage IIB-IV, untreated cHL were eligible. Pts received 2 'lead-in' doses of single-agent Bv 1.8 mg/kg (q 3 weeks) followed by 6 cycles of standard AVD. Supportive antibiotics were encouraged & granulocyte growth factor was allowed. Responding pts proceeded to consolidation (Cx) therapy with 4 Bv cycles. Study design was a Simon 2-stage; the primary endpoint was CR rate after AVD (ie, prior to Bv Cx) using revised Cheson with FDG-PET; pts must have received 2 cycles of AVD to be evaluable for response. The study was considered promising if >70% of evaluable pts demonstrated CR. Univariate & multivariate analyses (MVA) were performed using Cox proportional hazard regression for associations between lab and clinical factors (including co-morbidities assessed by the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS)) with survival.
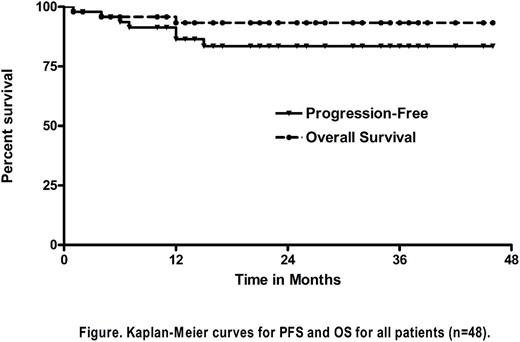
Results: 48 pts enrolled to the study (8/2012-8/2016) with 41 being evaluable for response. Characteristics for all pts included: median age 69 yrs (60-88); 30M:18F; median ECOG PS of 1 (21% PS=2); 82% stage III/IV disease (bone marrow involved 23%); and IPS 3-7 in 60%. No pts had loss of activities of daily living (ADL) at baseline, while 12% had loss of instrumental ADLs. Median CIRS co-morbidity score at baseline was 6 (0-20). 6 pts received <2 cycles of AVD and were non-evaluable for response for the following reasons: toxicity in cycle 1 AVD, wound infection and syncope (n=2); withdrew consent (n=2); hepatic toxicity to BV lead-in (n=1) & grade 5 pancreatitis with Bv lead-in (n=1) (Gandhi et al Blood 2014). Notably, the median pre-treatment CIRS score among pts who received <2 cycles of AVD (due to toxicity and/or consent withdrawal) was 13 (10-19) vs 5 (0-20) for pts who received 2 or more AVD cycles as planned (P=0.001). Collectively, 52% of pts completed all 12 intended cycles and 65% received at least 1 Bv Cx treatment as planned. Median CIRS for pts who completed all cycles of Bv-AVD was 4 vs 8 for pts who did not (P=0.03). The overall response rate (ORR) to the initial 2 doses of Bv 'lead-in' was 87% with 30% CR rate. After completion of AVD, the ORR and CR rates for evaluable pts were 95% and 90%, respectively. One pt improved response after consolidation yielding a post-Cx CR rate of 93%. By intent-to-treat (ITT) including all n=48 pts, ORR and CR rates were 88% and 81%, respectively. With median follow-up of 24 months (6-46), 2-yr PFS for evaluable pts was 90%. On ITT of all 48 pts, the 2-yr PFS rate was 85% with corresponding 2-yr OS of 94% (Figure). 42% of all pts experienced a serious adverse event (AE). Grade 3/4 AEs occurring in >1 pt were neutropenia (60%); infection (15%), febrile neutropenia (8%); transaminitis (6%); renal insufficiency (6%); urinary infection (6%); pneumonia (6%); hyponatremia (6%); fatigue (6%); febrile neutropenia (6%); diarrhea (4%); pancreatitis (4%), & peripheral neuropathy (PN) (4%). 33% of all pts experienced grade 2 PN (6% motor/27% sensory); the majority were reversible. Treatment related mortality on study was 2% (n=1 pancreatitis). Reasons for study discontinuation were: completed treatment (52%); toxicity/AEs (33%); withdrew consent/refused additional treatment (9%); & progressive disease or death (6%). Finally, for pt prognostication, increasing age (continuous) (P=0.005), female (P=0.05) & increased CIRS (continuous) (P=0.006) were associated with inferior PFS on univariate analysis; on MVA, only increasing age remained significant (HR 1.19 per yr >60, 95%CI 1.02-1.37, P=0.02).
Conclusions: Bv-AVD incorporating Bv sequentially before and after chemotherapy represents among the best-reported outcomes to date for untreated older cHL pts. Efforts to maintain these robust remission and survival rates, but with less toxicity, should be a focus of ongoing investigation. This should include response-adapted design and integration of other novel agents (eg, checkpoint inhibitors), especially for pts with advanced ages and/or multiple co-morbidities.
Evens: Novartis: Consultancy; Affimed: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Millennium: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; • Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Advani: Spectrum: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Agensys: Research Funding; Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Kura: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Nanostring: Consultancy; FortySeven: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Cell Medica: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Sutro: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Fanale: ONYX: Research Funding; CELGENE: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; TAKEDA: Honoraria, Research Funding; AMGEN: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; SEATTLE GENETICS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; GENENTECH: Research Funding; MERCK: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; MOLECULAR TEMPLATES: Research Funding; ADC THERAPEUTICS: Research Funding. Winter: Merck: Research Funding; Glaxo-Smith-Kline: Research Funding. Gordon: Janssen: Other: Data Monitoring Committee. Hamlin: Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Portola: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: research support; Incyte: Other: research support; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Other: research support; Seattle Geneitcs: Other: research support.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract